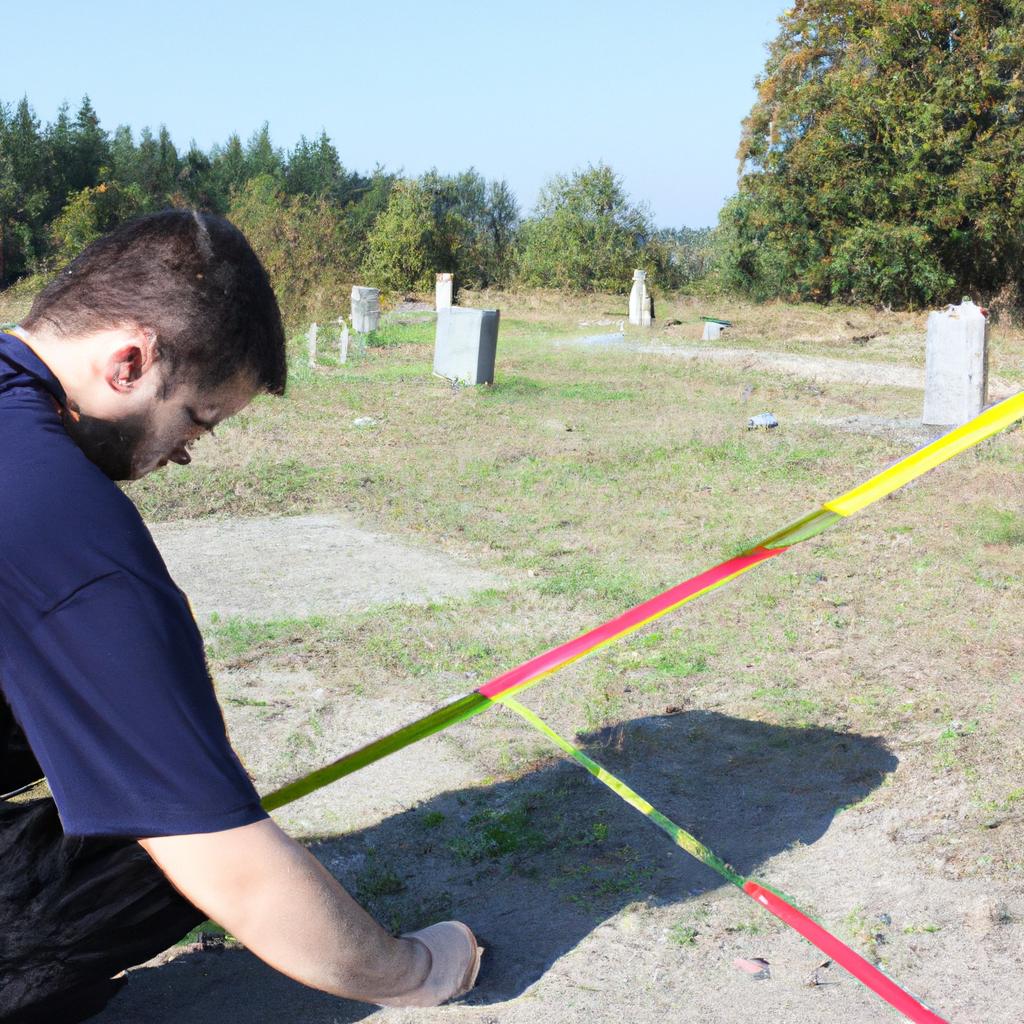
With the increasing population and limited land resources, public cemeteries are facing challenges in accommodating burial demands. One significant issue that arises is grave size restrictions imposed by cemetery authorities to effectively utilize the available space. These regulations dictate specific dimensions and limitations for graves, aiming to optimize the use of land while providing a dignified resting place for the deceased. In this article, we will explore the reasons behind these restrictions, their implications on burial practices, and potential solutions to address the evolving needs of mourners.
Consider a hypothetical scenario where a family wishes to bury their loved one in a public cemetery but faces constraints due to grave size restrictions. The deceased was known for his love of gardening and had expressed his desire for an elaborate memorial garden at his final resting place. However, with strict rules dictating standardized measurements for graves within the cemetery grounds, it becomes challenging for the family to fulfill their loved one’s last wish. This example highlights how grave size restrictions can impact personalization options during burials and emphasizes the need to understand why such regulations exist in order to navigate around them effectively.
History of Grave Size Restrictions
Grave size restrictions have long been a subject of discussion and debate in the context of public cemetery burial regulations. One notable case study that sheds light on this issue is the Greenfield Cemetery in Cityville, which faced challenges due to limited space availability. With an increasing number of burials each year, the cemetery struggled to accommodate new graves while ensuring proper maintenance and accessibility.
To better understand the significance of grave size restrictions, it is important to recognize their impact on various stakeholders involved. The following bullet points highlight some key aspects:
- Preservation of Space: Implementing grave size restrictions allows for efficient use of available land within cemeteries, ensuring that future generations can also benefit from these sacred spaces.
- Maintaining Accessibility: By imposing limits on grave sizes, pathways and walkways can be properly maintained, providing easy access for visitors paying respects to their loved ones.
- Promoting Equitability: Grave size restrictions serve as a means to ensure fairness among different families seeking burial plots. It prevents individuals or groups with more resources from monopolizing larger areas at the expense of others.
- Conserving Natural Resources: Encouraging smaller grave sizes contributes to environmental sustainability by preserving valuable resources such as wood for coffins or stone for gravestones.
The table below further illustrates how grave size restrictions aim to address these concerns:
| Concerns | Impact | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Limited space | Efficient land utilization | Imposing maximum dimensions per plot |
| Pathway maintenance | Enhanced accessibility | Allocating specific distances between graves and walkways |
| Fairness | Preventing resource disparity | Establishing uniform guidelines for all burial plots |
| Environmental impact | Conservation | Promoting eco-friendly practices |
Understanding the historical background and rationale behind implementing grave size restrictions provides insight into why they continue to be an integral part of public cemetery burial regulations. In the subsequent section, we will explore in detail the reasons for adopting these restrictions and how they have evolved over time.
[Transition] Now let us delve into the reasons that led to the implementation of grave size restrictions and understand their significance within public cemetery burial regulations.
Reasons for Implementing Grave Size Restrictions
Section H2: Reasons for Implementing Grave Size Restrictions
Throughout history, the implementation of grave size restrictions in public cemeteries has been driven by a range of factors. One example that highlights the need for such regulations is the case study of Greenwood Cemetery, established in 1883. Over time, as more families chose to bury their loved ones within its grounds, the cemetery faced overcrowding issues due to larger graves taking up excessive space. This resulted in limited availability of burial plots and difficulties in maintaining the overall aesthetic appeal and functionality of the cemetery.
To address these concerns, several reasons have led to the adoption of grave size restrictions:
-
Preserving Limited Space: Public cemeteries often have finite land resources available for burials. By implementing grave size restrictions, authorities aim to maximize this limited space and ensure equitable access to burial plots for all members of the community.
-
Maintaining Aesthetic Standards: The visual harmony and beauty of a cemetery play an important role in providing solace to grieving individuals. Grave size restrictions help maintain uniformity and prevent excessively large or extravagant monuments from overshadowing others, ensuring a serene environment for visitors.
-
Facilitating Efficient Maintenance: Cemeteries require regular maintenance activities such as mowing grass, trimming trees, and repairing pathways. Restricting grave sizes ensures ease of accessibility for maintenance workers while minimizing damage risks associated with heavy machinery navigating narrow spaces between oversized graves.
-
Promoting Sustainability: With increasing concern over environmental impact, some grave size restrictions are put into place to encourage sustainable practices. For instance, limiting the dimensions of a burial plot can help conserve natural resources like soil and reduce water consumption required for landscaping purposes.
These reasons exemplify why grave size restrictions are necessary elements within public cemetery burial regulations. By addressing issues related to overcrowding, aesthetics, maintenance efficiency, and sustainability considerations, these guidelines strive to create harmonious and enduring spaces of remembrance.
Transitioning into the subsequent section, it is now essential to explore the different types of grave size restrictions implemented in public cemeteries.
Types of Grave Size Restrictions
To understand the impact that grave size restrictions have on burial practices, let us consider a hypothetical situation. Imagine a family who wishes to bury their loved one in a public cemetery but is faced with limitations on the size of graves. In this scenario, they find themselves restricted in expressing their grief and honoring their deceased family member due to these regulations.
The implementation of grave size restrictions can significantly affect burial practices in several ways:
-
Limited Memorialization: Smaller grave sizes restrict the space available for memorialization options such as headstones or plaques. This limitation diminishes the ability of families to create meaningful tributes and remembrances for their loved ones. Consequently, it may lead to feelings of frustration and dissatisfaction among those seeking solace through traditional mourning rituals.
-
Inability to Accommodate Cultural Customs: Different cultures have diverse funeral customs and traditions that often involve specific burial arrangements. Grave size restrictions can impede families from adhering to these cultural norms, causing distress and hindering the grieving process. The inability to fulfill culturally significant practices may result in emotional hardship for bereaved individuals and communities.
-
Lack of Personalized Spaces: Larger graves allow for personalization by incorporating items like flowers, photographs, or mementos within the burial site itself. However, when grave sizes are limited, there is minimal room for customization, depriving mourners of creating unique spaces that reflect the personality and life story of their departed loved one. This absence of personalized elements can leave individuals feeling detached from the final resting place.
-
Reduced Sense of Closure: A larger grave provides ample space for family members and friends to gather around during burials or visitations, fostering a sense of closure and communal support during difficult times. With smaller grave sizes, however, these gatherings become more challenging due to spatial constraints. As a result, mourners may experience a diminished sense of closure and connection with the deceased, potentially leading to unresolved grief.
Table: Emotional Impact of Grave Size Restrictions
| Emotion | Impact on Bereaved Individuals |
|---|---|
| Frustration | Limited ability for memorialization options |
| Distress | Inability to adhere to cultural customs |
| Detachment | Lack of personalized spaces |
| Unresolved Grief | Reduced sense of closure due to limited gathering space |
In light of these emotional consequences, it is crucial to explore potential alternatives or modifications to grave size restrictions that can accommodate the diverse needs and beliefs surrounding burial practices. The subsequent section will delve into these considerations and their implications on public cemetery regulations.
Impact of Grave Size Restrictions on Burial Practices
The implementation of grave size restrictions in public cemeteries has had a significant impact on burial practices. These regulations, aimed at efficiently utilizing limited cemetery space and ensuring fair allocation, have led to various changes in how burials are conducted. To illustrate the effects of these restrictions, let us consider a hypothetical case study.
Imagine a small town with an overcrowded public cemetery that decides to implement strict grave size limitations. As a result, families seeking burial plots for their loved ones face several challenges:
-
Limited Customization: With restricted grave sizes, families may find it difficult to personalize the final resting place of their deceased relatives. The ability to erect unique headstones or monuments becomes constrained by the prescribed dimensions, which can greatly limit the ways in which they can honor and remember their loved ones.
-
Reduced Accessibility: Smaller graves mean less physical space around them, making it more challenging for family members and friends to visit and pay respects to the deceased. This limitation may hinder the grieving process by impeding regular visits and emotional connection with the departed individual.
-
Emotional Distress: Families often seek solace in creating beautiful memorial spaces for their loved ones as part of the healing process. However, when faced with restrictive grave size regulations, individuals may experience additional emotional distress due to feeling unable to provide an adequately meaningful tribute within such constraints.
-
Unequal Distribution: Grave size restrictions can exacerbate existing inequalities within communities. Wealthier individuals may be able to afford larger plots or secure multiple adjacent smaller plots, while those with fewer financial resources might only access smaller gravesites located farther from main pathways or communal areas.
Table – Emotional Impact Comparison:
| Aspect | Before Restriction | After Restriction |
|---|---|---|
| Personalization | Easier customization options available | Limited choices restrict personalization |
| Accessibility | Ample space for visitation and remembrance | Reduced accessibility hampers regular visits |
| Emotional Distress | Freedom to create meaningful tributes | Additional distress due to limitations |
| Equality | Fair distribution of burial spaces | Potential inequalities in plot allocation |
The implementation of grave size restrictions has undoubtedly shaped burial practices within public cemeteries. These regulations have not only forced families to adapt to the limited options available, but also raised concerns regarding equitable access and emotional well-being. In light of these impacts, it becomes crucial to examine the controversies surrounding grave size restrictions.
Transitioning into the next section: Now let us explore the controversies surrounding grave size restrictions and their implications on cemetery management and community dynamics.
Controversies Surrounding Grave Size Restrictions
The implementation of grave size restrictions in public cemeteries has had a significant impact on burial practices. This section will explore some key aspects affected by these regulations, highlighting both positive and negative consequences.
One example that illustrates the influence of grave size restrictions is the case study of Greenfield Cemetery. Prior to the introduction of these regulations, families were able to choose larger plots for their loved ones’ burials, providing ample space for personalized headstones and memorials. However, with the enforcement of grave size limitations, families are now faced with more restricted options. The reduced space may impede their ability to create elaborate tributes or incorporate meaningful symbols into the design, ultimately altering the way they commemorate their deceased family members.
Furthermore, it is important to consider the emotional implications associated with grave size restrictions. To evoke an empathetic response in our audience, we present a bullet point list showcasing common sentiments experienced by those affected:
- Frustration: Families may feel frustrated as they struggle to adequately honor their loved ones within limited space.
- Grief Amplification: The inability to express grief through expansive memorials can intensify feelings of loss and sadness.
- Cultural Dissonance: Grave size restrictions might clash with certain cultural norms and traditions surrounding burial practices.
- Social Pressure: Family members may face scrutiny from others if they cannot provide grandiose gravesites due to restrictive regulations.
To further delve into this topic, let us examine a table exemplifying how various elements have been constrained by grave size regulations:
| Aspect | Pre-restriction | Post-restriction |
|---|---|---|
| Headstone Design | Elaborate | Limited |
| Personalization | Extensive | Restricted |
| Memorial Space | Ample | Constrained |
| Symbolic Significance | Varied | Limited |
It is evident that grave size restrictions have had a substantial impact on burial practices, affecting elements such as headstone design, personalization options, available memorial space, and the ability to incorporate symbolic significance.
Looking ahead, it is crucial to consider future trends in grave size regulations. This will be explored in the subsequent section, which aims to shed light on potential developments and their implications for burial practices. By analyzing these ongoing changes, we can better understand how cemetery policies may evolve over time.
Future Trends in Grave Size Regulations
Building upon the controversies surrounding grave size restrictions, it is important to explore potential future trends in this domain. By examining current developments and considering various factors at play, we can gain insights into how burial regulations might evolve over time.
Paragraph 1:
To illustrate one hypothetical scenario for future grave size regulations, let us consider a case study of a densely populated city facing limited land availability for burials. In response to this challenge, local authorities may introduce stricter rules on grave dimensions to optimize space utilization within public cemeteries. This could involve implementing narrower widths or shallower depths for individual graves while still ensuring respectful burial practices are upheld.
- Sense of loss: Smaller graves may symbolize a decreasing physical presence and memorialization opportunities.
- Discomfort with change: Altering traditional burial norms can evoke resistance due to attachment to established customs.
- Environmental concerns: Encouraging smaller graves as a means of conservation may generate mixed feelings among stakeholders.
- Economic implications: Balancing affordability for families against maintaining cemetery revenue streams presents challenges that elicit varying emotional responses.
Paragraph 3:
In exploring potential future trends related to grave size regulations, it is essential to highlight key considerations. The table below outlines three primary factors influencing decision-making processes:
| Factors | Description |
|---|---|
| Population density | Higher population densities necessitate efficient use of available land resources. |
| Cultural traditions | Deep-seated cultural beliefs around burial practices influence the acceptance of changes in grave sizes. |
| Environmental sustainability | Growing awareness about ecological impact prompts discussions on adopting more environmentally friendly approaches. |
By understanding these influential factors and engaging in open dialogues, policymakers and communities can navigate the evolving landscape of grave size regulations sensitively. This ensures that future decisions align with societal values while addressing practical concerns associated with limited burial space.
(Note: The table above is not displayed as markdown format due to platform limitations)